Diabetes Management Using Glucose Monitoring Devices | TechSci Research
According to the World Health Organization statistics, currently approx. 463 million people are living with diabetes throughout the world. The number is set to rise to some 700 million by 2045. Diabetes is one of the leading causes of death globally, accounting for more than 79,000 deaths annually. The growing prevalence of diabetes worldwide due to poor lifestyle, inadequate physical activity, stress, obesity, smoking, and other factors are increasing the need for new diagnostic tools and treatments to keep the insulin levels in check. Monitoring blood sugar levels is an integral part of diabetes management. With the increasing incidences of diabetes, many biotech companies are coming up with innovations for patients to check their insulin and take necessary steps conveniently.
Blood Sugar Lancing Device
Despite significant technological advancements, fingerpick blood sugar tests remain the no.1 choice for people who have diabetes. The lancing device requires pricking finger with a small, sharp needle, which have to be put up on a test strip. The strip then needs to be put into a meter that displays the sugar levels within a few seconds. The lancing devices are highly sophisticated and portable so that patients can carry the device anywhere at any time.
The new glucometers available in the market enable patients to test sites other than fingertips such as the upper arm, forearm, base of the thumb, and thigh. However, since blood sugar levels in the fingertips show changes more quickly, patients with the symptoms of hypoglycaemia should use fingertips for more accurate readings. The patients can take the fingerpick test anytime when they feel their blood sugar levels are low. With glucometers, patients need to keep records of their blood monitoring results to check for patterns, which the caregivers can utilize to check how their body reacts to certain foods, exercise, or medicines.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems
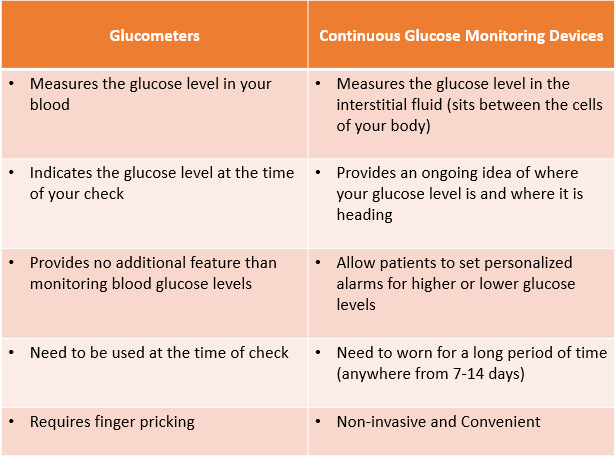
In the last few years, many technologies have been introduced in the market that allow non-invasive painless blood glucose monitoring. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGMs) devices are amongst the recent advances in diabetes management technologies designed to provide patients with real-time information about glucose levels in the body. People with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes have the option to easily manage their chronic condition by easily tracking the insulin levels that go up and down.
Since many factors come into play when it comes to fluctuating glucose levels, such as the kind of food you eat, sports you play and your overall lifestyle, sometimes healthcare providers are unable to find out the body's reaction to certain things. However, continuous glucose monitoring is equipped with a sensor that detects the blood sugar levels in the fluid under the skin over time while the patient is wearing the device. The patient can obtain glucose readings as frequently as desired using a reader or smartphone with great convenience in a painless manner. CGMs can record glucose levels throughout 24 hours and show glucose patterns over two weeks, which patients, as well as caregivers, can access.
The continuous glucose monitoring device requires the sensor to be attached to a transmitter held on the skin with a sticky patch. The sensor wirelessly transmits data to a small recording device (or a smartphone), which the patients can easily carry in their clothing, purse, bag, etc. The patients have the flexibility to remove the sensor and replace it on a different part of the body every 7 to 14 days. The implantable sensors can last up to 90 days, but they need to be re-inserted and removed by the physician or other care provider. The real-time CGM devices automatically display blood glucose levels every five minutes, and the receiver also triggers the alarm when they reach a level above or below a preset level.
Here are some of the Latest Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Changing the Lives of People Suffering from Diabetic Conditions
Dexcom G6
Dexcom G6 runs on a new algorithm that enhances the accuracy of the sensors and reduces the lag time between the sensor level and blood glucose levels compared to its previous models. Patients can trust the device to provide reading accurate enough to dose insulin without calibrations. Besides, the CGM device has a pain-free insertion and enables customizable alerts.
Pros
- Keeps the patients informed about their glucose levels
- Readings are not affected by acetaminophen
- The device is covered by Medicare
- Approved for all the users above the age of 2
- Transmitter lasts up to 3 months
Cons
- Sensors need to be changed every ten days
- Require up to 2 hours of warm uptime
- Sensors are not reusable
Abbott's FreeStyle Libre
Approved in 2017, FreeStyle Libre was the first continuous glucose monitor that does not require finger pricks. The sensor of the CGM device has to be worn on the back of your upper arm and lasts up to 14 days. The CGM device can store glucose readings for up to 90 days, and the sensor can store data for up to 8 hours.
Pros
- Does not require calibrations
- Warmup time of one hour
- Can be used with the reader
- Allows sharing of data with caregivers
- Can be used with a reader or a smartphone
Cons
- Reader needs to be changed every seven days
- Does not have alerts or alarms
- High levels of aspirin and vitamin can interfere with readings
- Only approved for users above the age of 18
Medtronic Guardian Sensor 3
Medtronic’s insulin pumps, and continuous glucose monitoring devices are available with 670G integration with an approved sensor for seven days. The device enables customizable alerts for different times and days. The smartphone-compatible device can be used without an insulin pump and does not require a separate receiver to connect with your smartphone. The CGM device has a different transmitter attached to each sensor, but rechargeable and lasts for a year.
Pros
- Includes predictive alarms for blood sugar is too high or low
- Can be connected with both Android and iPhone apps
- Cans share your glucose data
- Can be easily inserted with a one-button insertion device
- Displays past glucose data and patterns
Cons
- Requires fingerstick calibrations
- Requires 2-hour warmup period
- Sensors cannot be reused
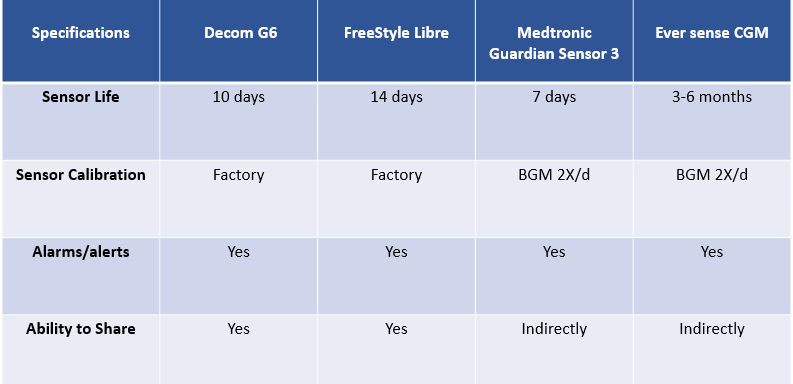
Eversense Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device
Eversense implantable CGM device is the first glucose sensor available in the size of a small twig, which is implanted under the skin for up to 90 days for monitoring the glucose readings in real-time. Unlike other CGMs in the market, Eversense provides glucose monitoring for up to 90 days and comes with a removable and rechargeable smart transmitter.
Pros
- On-body vibration alerts for very low or high sugar levels
- Chargeable and water-resistant transmitters
- FDA-approved for dosing decisions
- Lasts up to 90 days under the skin
Cons
- Require two-finger calibrations per day
- Removing and adhering to the transmitter takes at least 10 minutes every day
- Not yet approved for children’s use
Upcoming Developments in Diabetes Management Therapy
People living with diabetes have to face the brunt of injecting insulin which can be painful and tiring. Now, many drug manufacturers are developing insulin pills that can be credible alternatives to insulin injection as the patient does not have to bear the pain of injections for insulin administration, essential to maintain adequate blood sugar levels for people with diabetes.
Insulin is a complex protein that degrades in the stomach and small intestine, making the insulin pills introduced earlier unsuccessful for diabetes management. However, now many manufacturers are developing insulin pills that reach directly to the liver, where it releases the hormone that mimics endogenous insulin's action. Insulin pills could make diabetes management quite convenient and affordable, eliminating the pain of needles and reducing healthcare expenditure for the patients. Leading pharmaceutical companies are using protein engineering to develop the insulin pill so that it can navigate the stomach without breaking down. Currently, only two insulin pills developed by Oramed and HDV-1 have been approved by the FDA for administration. In addition, other insulin delivery methods are also under development to make insulin administration painless and relatively inexpensive than pumps.
Conclusion
More and more technologies are marking an entry into the market to help people manage diabetes properly. Future therapies such as new drugs, islet cell transplantation, artificial pancreas, electronic skin patch and digital contact lenses are anticipated to improve diabetes management for type-1 and type-2 diabetes patients. Besides, many wireless glucometers are being introduced for patients to perform effective glucose monitoring.
Comments
Post a Comment